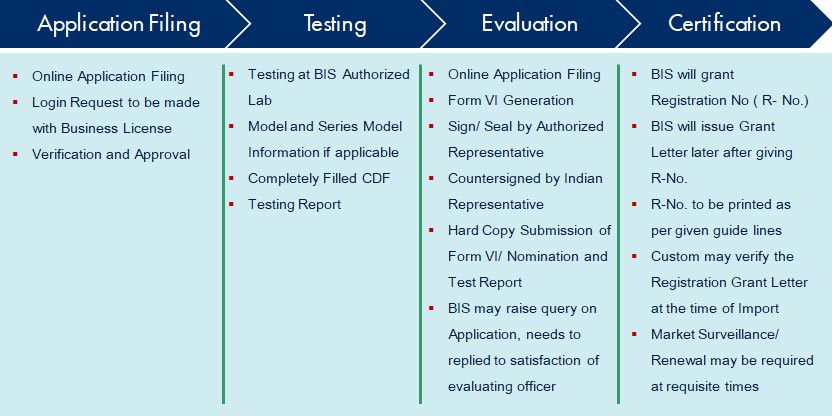
CSR was introduced by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY) in Y2012, along with Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). The scheme then started covering 15 electronic and consumer products and added more products in subsequent notifications. Under this scheme it is made mandatory for manufacturers to get their products registered before launching them in market.
The products are tested for safety as per the applicable IS standard. Overseas Manufacturers are required to have a local representative in India.
This program is for the manufacturer and unique registration is granted for each manufacturing location.
To make this program robust, Market Surveillance has been designed to ensure compliance. MeitY's authorised representatives will pick the product from the market and send it to designated lab for testing and verification.
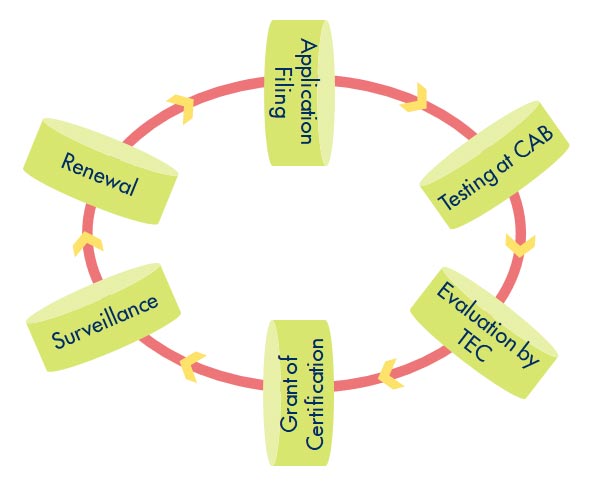
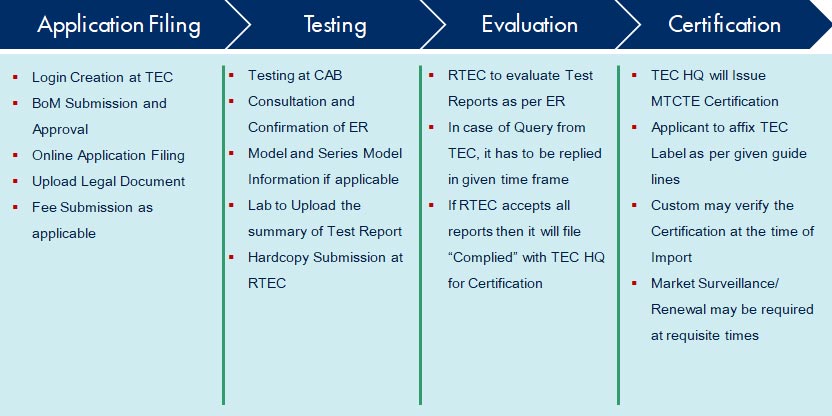
Telecommunication Engineering Centre (TEC) functions under Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India.
The products are tested for safety as per the applicable IS standard. Overseas Manufacturers are required to have a local representative in India.
This program is for the manufacturer and unique registration is granted for each manufacturing location.
For the purpose of testing, four Regional Telecom Engineering Centers (RTECs) have been established which are located at New Delhi, Bangalore, Mumbai, and Kolkata.
With the notification of Indian Telegraph (Amendment) Rules 2017 enabling mandatory testing and certification of telecom equipment (MTCTE), TEC has been designated as the Telegraph Authority for the purpose of administration of MTCTE procedure and Surveillance Procedure, and for formulation of Essential Requirements under MTCTE.

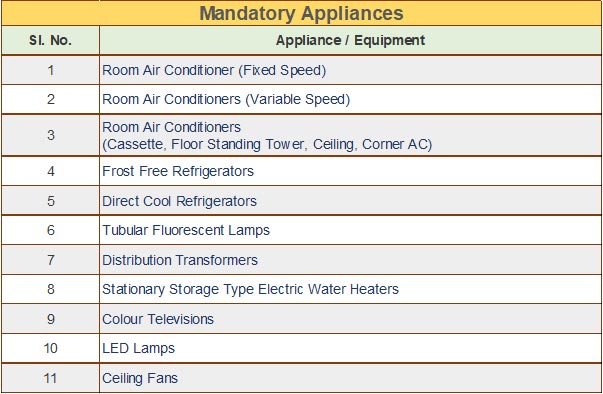
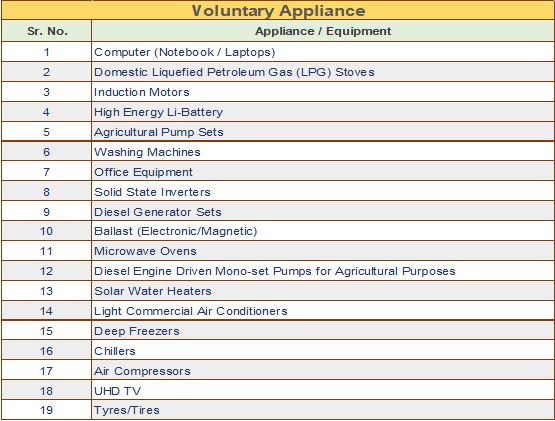
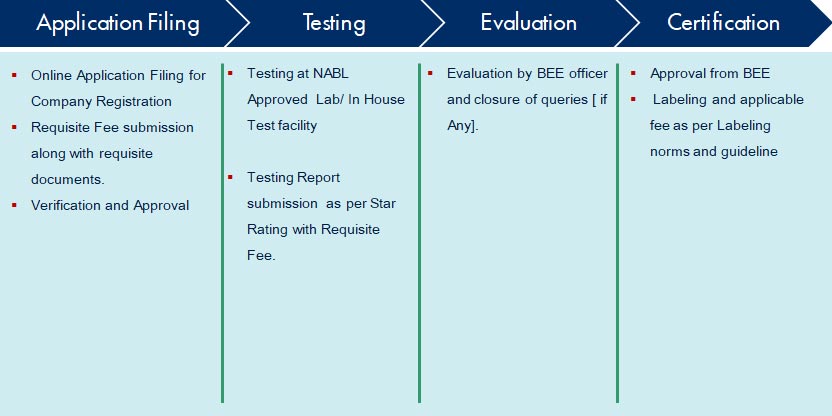
The Government of India has set up Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) on 1st March 2002 under the provision of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001. The mission of Bureau of Energy Efficiency is to assist in developing policies and strategies with a thrust on self-regulation and market principles with the primary objective of reducing energy intensity of the Indian economy within the overall framework of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001. This will be achieved with active participation of all stakeholders, resulting into accelerated and sustained adoption of energy efficiency in all sectors.
BEE co-ordinates with designated consumers, designated agencies and other organizations and recognize, identify and utilize the existing resources and infrastructure, in performing the functions assigned to it under the Energy Conservation Act. The Energy Conservation Act provides for regulatory and promotional functions.
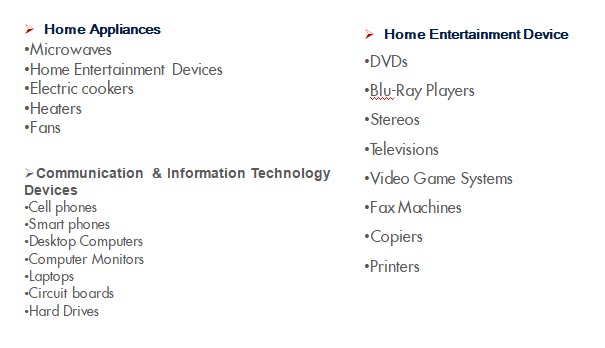
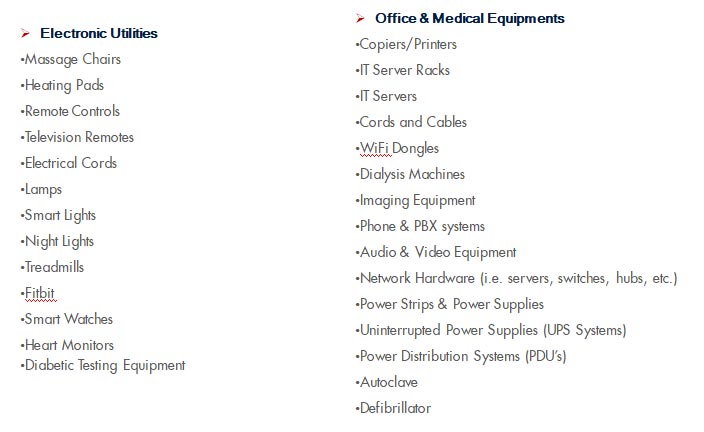
Electronic waste or e-waste describes discarded electrical or electronic devices. It is also commonly known as waste electrical and electronic equipment.
E-waste management is a process to collect e-waste, recover and recycle material by safe methods, dispose of e-waste by suitable techniques to reduce its adverse impacts on environment.
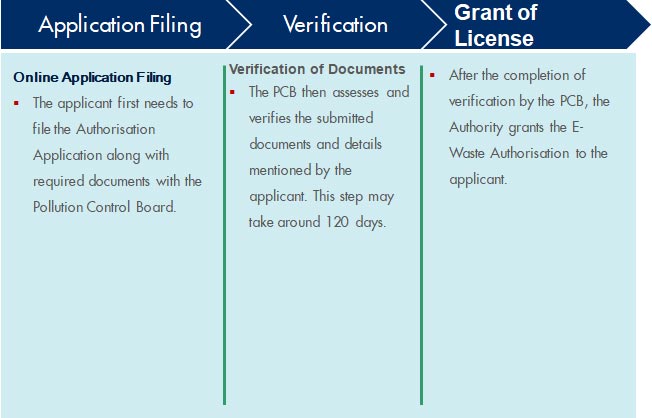
The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change issued E-Waste (Management) Rules 2022 on November 2, 2022. This will go into effect on April 1, 2023.
As per this regulation, all manufacturers, producers, refurbishers, and recyclers shall have to register on the portal and collect e-waste generated during the manufacturing, refurbishing, or disposal of any electrical and electronic equipment and ensure its recycling or disposal. The Entities must register on the portal under the appropriate category, such as manufacturer, producer, refurbisher, or recycler. If an entity falls into more than one category, it must register under each category separately. It is illegal for any entity to conduct business without registration.